Table of Contents
When it comes to electrical installations, understanding the difference between a distribution box and a junction box is crucial for safety, efficiency, and proper circuit management.
Although these two components are often found in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, they serve distinct purposes and are engineered for different scenarios.
In this article, we’ll explore their unique roles, structural differences, and typical applications.
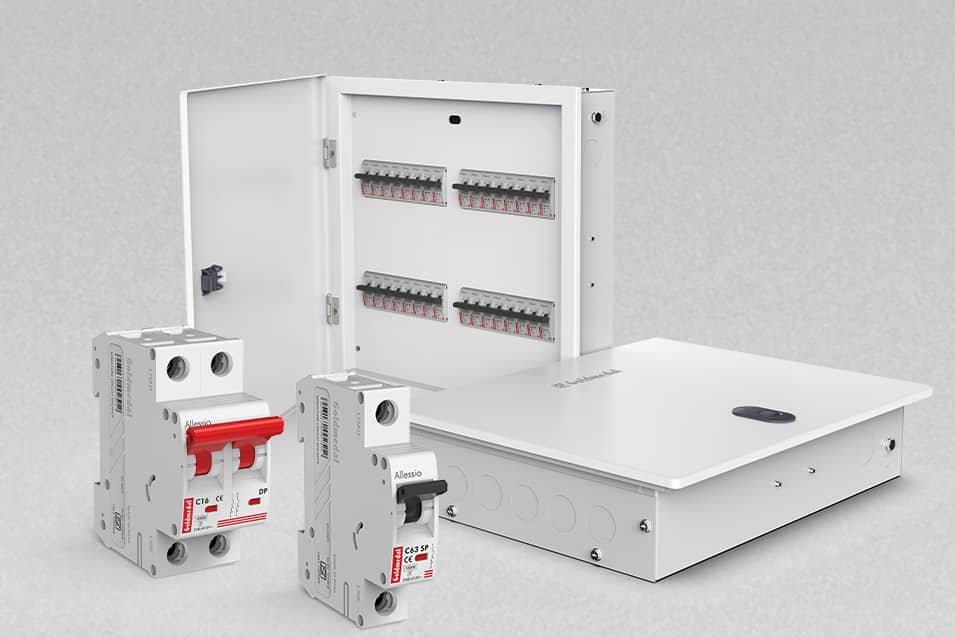
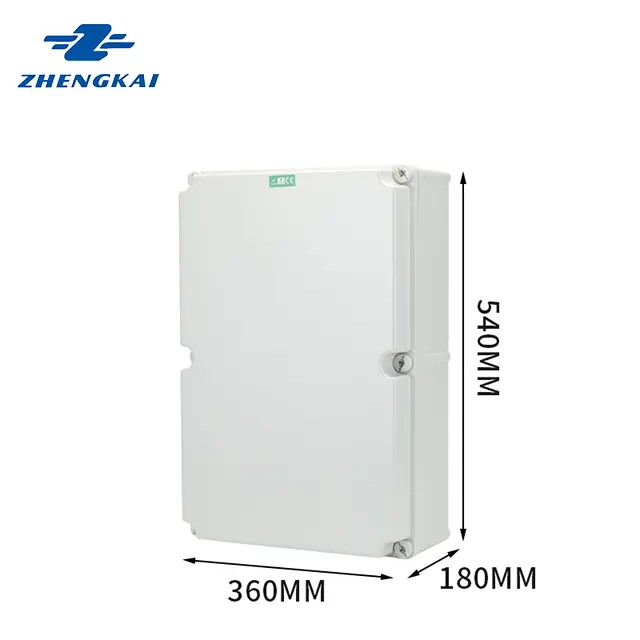
What Is a Distribution Box?
A distribution box is a key component in any electrical system where power needs to be distributed, controlled, and protected. Its main functions include:
- Distributing the main power supply to various branch circuits.
- Providing essential safety features such as overload protection, short-circuit protection, and leakage protection.
- Withstanding high voltages and currents, making it suitable for demanding environments.
Distribution boxes are commonly found in large buildings, factories, commercial complexes, and residential power distribution systems.
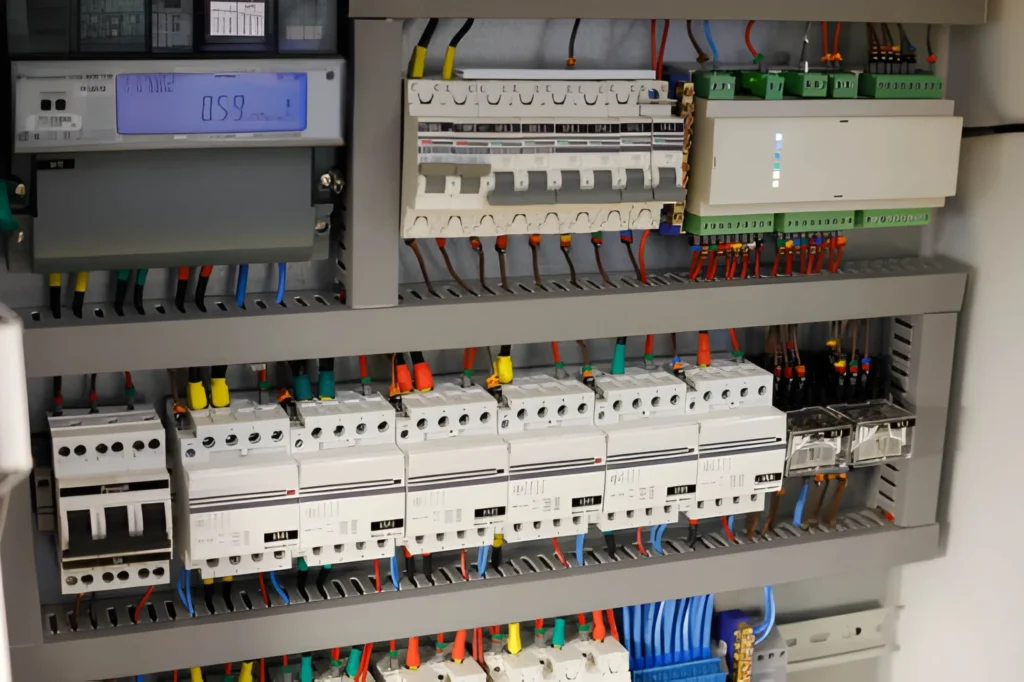
Inside a distribution box, you’ll typically find components like circuit breakers, fuses, switches, and sometimes power metering devices.
These elements work together to ensure that each circuit receives the correct amount of power and is protected against electrical faults.
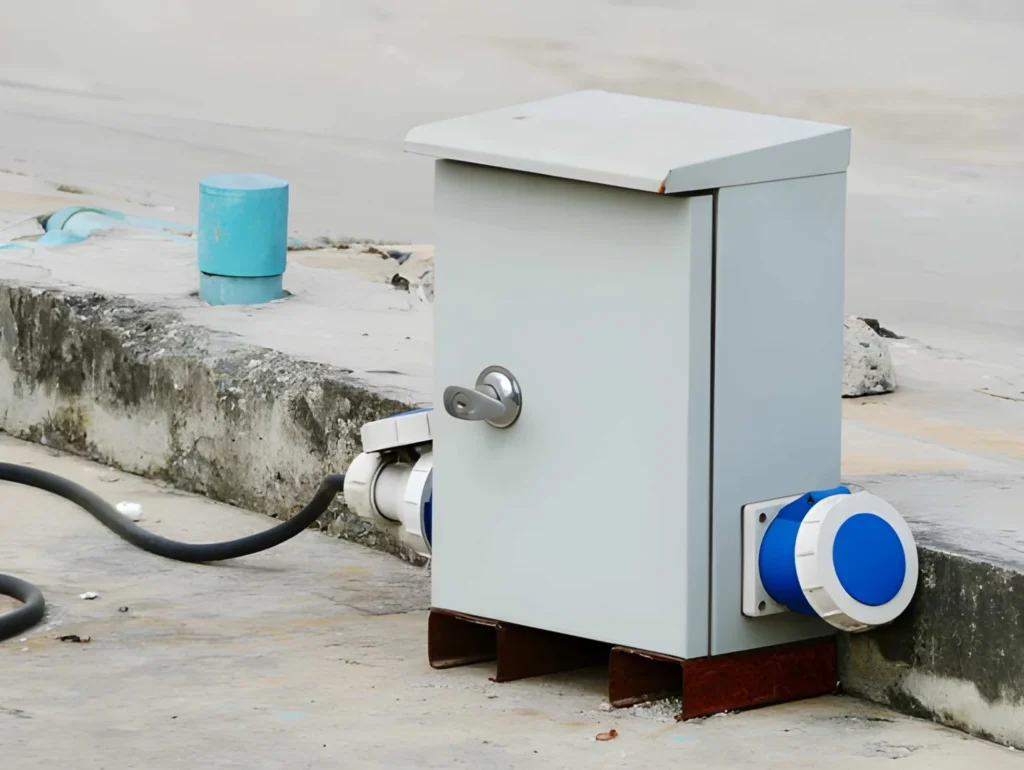
What Is a Junction Box?
A junction box, on the other hand, is primarily used for connecting wires within an electrical circuit. Its main purposes are:
- Providing a safe enclosure for wire connections, especially at points where wires branch off or change direction (such as corners or long cable runs).
- Protecting the connections from dust, dirt, and other environmental factors.
- Ensuring reliable electrical contact at the junction points.
Junction boxes are generally designed for lower voltage and current capacities compared to distribution boxes.
They are ideal for use in smaller buildings, residential wiring, and commercial real estate where the primary need is to connect and protect wires rather than distribute or control large amounts of power.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Distribution Box | Junction Box |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Power distribution, control, and protection | Circuit connection and wire protection |
| Components | Circuit breakers, fuses, switches, meters | Terminal blocks, connectors |
| Power Capacity | High voltage and current | Low to moderate voltage and current |
| Application | Large buildings, factories, commercial systems | Homes, small offices, local circuit branching |
| Protection | Overload, short-circuit, leakage | Basic enclosure from dirt and contact |
| Complexity | Complex, multifunctional | Simple, single-purpose |
Usage Scenarios
Distribution Box:
Used where multiple circuits need to be managed and protected, such as in the main electrical room of a building, or at the entry point of power in a factory.
Junction Box:
Installed at points where wires are joined, split, or redirected-such as in ceilings, behind walls, or at corners of a wiring conduit system.
Distribution Box and Junction Box Structural Differences
- Distribution boxes are built to house multiple functional components, including devices for switching, protection, measurement, and control. They are often larger and more robust to accommodate these features.
- Junction boxes are simpler, typically just providing a safe enclosure for wire connections and sometimes temperature sensors. Their design focuses on accessibility and protection of the wire junctions rather than active control or distribution1
Conclusion
While both distribution boxes and junction boxes are essential for safe and efficient electrical installations, their roles are clearly defined:
- Distribution boxes manage, distribute, and protect electrical power across multiple circuits, handling higher power levels and offering comprehensive safety features.
- Junction boxes serve as protective enclosures for wire connections, ensuring safe and reliable circuit continuity in lower-power applications.
Understanding the difference between a distribution box and a junction box ensures that each is used appropriately, enhancing both the safety and reliability of your electrical system.