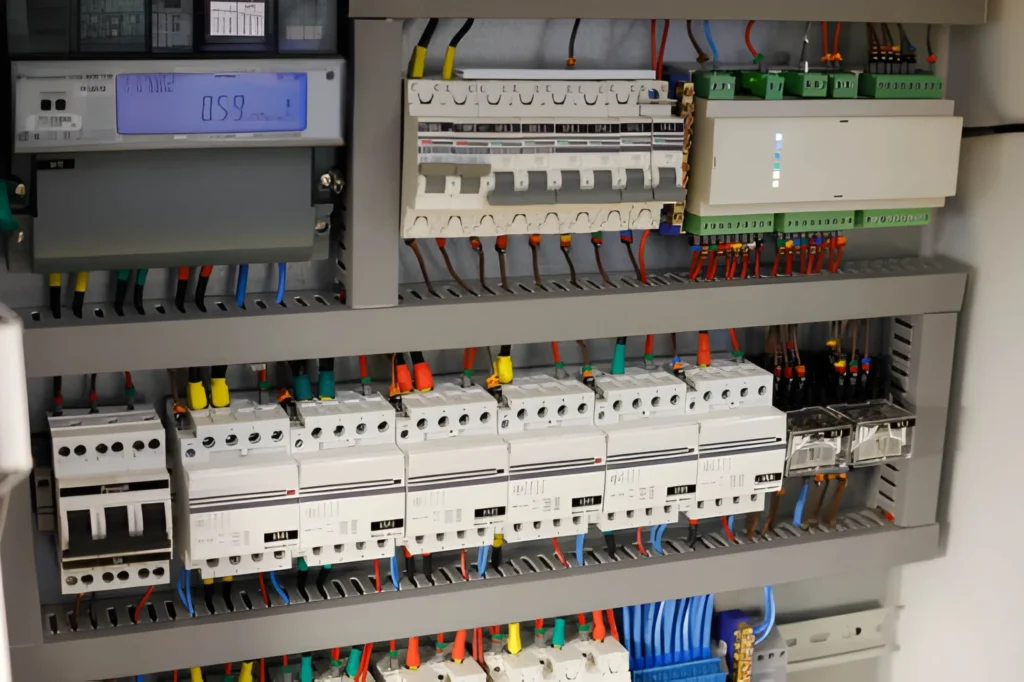
Have you ever wished your electrical panel could tell you what is happening inside your building? That simple question is why smart circuit breakers are rapidly moving from “nice to have” to “necessary” in modern electrical systems.
Traditional breakers protect you when something goes wrong. Smart circuit breakers go further. They protect, measure, communicate, and even help you optimize energy use. Whether you manage a factory, design a commercial building, or upgrade a home, these devices change how you think about electrical safety and reliability.
In this article, we will walk you through what smart circuit breakers are, how they work, where they are used, and how you can evaluate them with confidence. By the end, you should feel equipped to make a clear, practical decision instead of drowning in technical jargon.
What are smart circuit breakers?
At their core, smart circuit breakers are protective devices that combine traditional overcurrent protection with digital intelligence. Like conventional breakers, they interrupt current when they detect overloads, short circuits, or ground faults. Unlike conventional breakers, they also include sensors, processors, and communication modules that collect and transmit data in real time.
Think of a traditional breaker as a silent guard. A smart circuit breaker is a guard with a smartphone. It still stops problems, but it also tells you what happened, when it happened, and sometimes why it happened.
Key differences include:
- Built-in current and voltage sensing
- Real-time energy monitoring
- Remote control via apps or cloud platforms
- Integration with building management systems
A quick way to remember it: protection plus visibility equals intelligence.
| Feature | Traditional Breaker | Smart Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Overcurrent protection | Yes | Yes |
| Energy monitoring | No | Yes |
| Remote control | No | Yes |
| Data logging | No | Yes |
| IoT integration | No | Yes |
How do smart circuit breakers actually work?
Inside a smart circuit breaker, you will typically find three layers working together.
First is the protection layer. This is similar to what you already know: thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms that respond to overloads and short circuits. In many modern models, digital trip units replace purely mechanical parts for higher precision.
Second is the sensing layer. Current transformers, voltage sensors, and temperature sensors continuously measure electrical conditions. These sensors feed data to a microcontroller inside the device.
Third is the communication layer. Depending on the model, this may use Wi-Fi, Ethernet, RS-485, Zigbee, or other industrial protocols. The breaker sends data to a local display, a mobile app, or a cloud dashboard.
When something abnormal occurs, the breaker can trip automatically. At the same time, it can send you an alert on your phone. In advanced systems, it can even trigger other devices, such as disconnecting non-essential loads.
Key smart features you should know
Not all smart circuit breakers are created equal. Features vary widely, so understanding what matters is critical.
Real-time energy monitoring
Many devices measure kWh, voltage, current, and power factor. This turns your panel into a mini energy management system. You can see which circuits consume the most power and identify inefficiencies.
Remote control and automation
You can switch circuits on or off from anywhere. This is valuable for maintenance, emergency response, and demand management. Some systems allow scheduling or rule-based automation.
Fault diagnostics
Advanced models distinguish between overloads, short circuits, arc faults (AFCI), and ground faults (GFCI or RCD functions). Clear fault classification reduces troubleshooting time.
Load management
In facilities with limited capacity, smart circuit breakers can shed non-critical loads automatically to prevent total blackouts.
Data logging and analytics
Historical data helps you spot trends, predict failures, and support preventive maintenance.
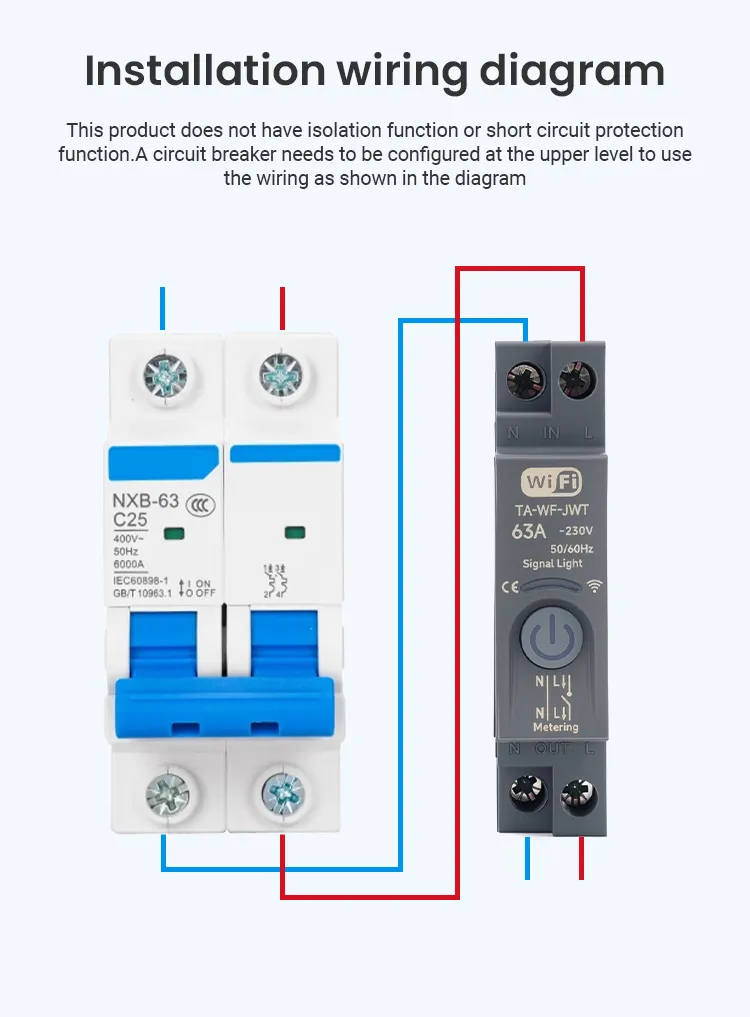

Types of smart circuit breakers
Smart circuit breakers come in different form factors and ratings. Your choice depends on your application and panel design.
Residential models
These are usually DIN-rail mounted or plug-on types designed for home panels. They emphasize user-friendly apps, Wi-Fi connectivity, and energy visualization.
Commercial models
Often integrated with building management systems (BMS). They focus on reliability, network security, and compatibility with protocols like Modbus or BACnet.
Industrial models
These may be smart MCCBs (molded case circuit breakers) or air circuit breakers with digital trip units. They handle higher currents, harsh environments, and mission-critical loads.
| Type | Typical Use | Connectivity | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | Homes, apartments | Wi-Fi | Easy installation |
| Commercial | Offices, retail | Ethernet/RS-485 | System integration |
| Industrial | Factories, plants | Industrial fieldbus | High durability |
Where are smart circuit breakers used?
You will find smart circuit breakers in more places than you might expect.
Smart homes
Homeowners use them to track appliance energy use, prevent nuisance trips, and improve safety. They are especially useful in homes with solar panels and battery storage.
Commercial buildings
Facility managers rely on them for energy optimization and predictive maintenance. They help reduce downtime and operating costs.
Data centers
Here, visibility is everything. Operators monitor each rack’s power draw and react instantly to anomalies.
Manufacturing plants
In industrial use cases, smart circuit breakers support condition-based maintenance. They can flag issues before equipment fails.
Renewable energy systems
In solar and microgrid installations, they provide fast protection and detailed performance data.
Technical specifications that matter
Choosing the right smart circuit breaker requires attention to a few key specs.
Rated current and breaking capacity
Make sure the device matches your system’s voltage and fault levels. Undersized breakers are a serious risk.
Form factor
Check whether your panel supports DIN rail, plug-on, or fixed-mount devices.
Communication protocol
If you need integration with existing systems, compatibility with your network is essential.
Accuracy of metering
Look for clear statements about measurement accuracy, especially if you plan to use the data for billing or compliance.
Cybersecurity
For networked devices, encryption and secure authentication are not optional.
| Spec | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Rated current | Matches your load |
| Breaking capacity | Ensures safe interruption |
| Protocol | Enables system integration |
| Metering accuracy | Supports reliable analytics |
| Security | Protects your network |
Installation and compatibility considerations
Installing smart circuit breakers is not radically different from installing traditional ones, but there are extra steps.
You need stable power for the electronics inside the breaker. Some models draw power from the line they protect, while others require auxiliary supply.
You also need network connectivity. In homes, this usually means Wi-Fi. In commercial and industrial settings, wired connections are often more reliable.
Panel space matters. Smart units can be slightly larger than standard breakers. Always verify physical compatibility before purchasing.
If you are upgrading an existing panel, a qualified electrician should evaluate wiring, grounding, and safety clearances.
Benefits and potential limitations
Smart circuit breakers deliver clear advantages, but they are not perfect.
Benefits
- Improved safety through faster detection
- Better energy visibility
- Reduced downtime
- Data-driven maintenance
- Remote control convenience
Limitations
- Higher upfront cost
- Dependence on connectivity
- Potential cybersecurity risks if poorly implemented
- Learning curve for new users
If your priority is pure protection at the lowest cost, traditional breakers may still make sense. If your priority includes efficiency, reliability, and insight, smart circuit breakers are hard to beat.
How to choose the right smart circuit breaker
Start with your objective. Are you focused on safety, energy savings, or operational reliability?
Next, define your environment. Residential, commercial, and industrial settings have different needs.
Then, evaluate compatibility. Check voltage, current ratings, panel type, and communication requirements.
Finally, consider the ecosystem. A breaker that works seamlessly with your existing software or BMS often delivers more value than a standalone device.
If you are planning a new installation or retrofit and want tailored guidance, you can always reach out to us for technical clarification or a quote that matches your exact requirements.
Conclusion
Smart circuit breakers represent a significant evolution in electrical protection. They still perform the essential task of preventing dangerous faults, but they add layers of intelligence that make your electrical system more transparent, controllable, and resilient.
By understanding how they work, what features to prioritize, and which specifications matter most, you can move beyond guesswork and make a confident, informed choice. Whether your goal is safer homes, smarter buildings, or more reliable factories, these devices give you the tools to see, act, and improve rather than simply react.
FAQ
What is the difference between an electric power meter and a smart circuit breaker?
An electric power meter measures total energy consumption at a service point, while a smart circuit breaker protects and monitors individual circuits. They complement each other in modern power systems.
Can smart circuit breakers replace electric power meters?
No. They provide detailed circuit-level data, but utilities still require certified electric power meters for official billing.
Do electric power meters work with smart circuit breakers?
Yes. Many energy management platforms integrate data from both electric power meters and smart circuit breakers to provide a complete view of consumption.
How accurate are modern electric power meters?
Most certified electric power meters achieve accuracy classes between 0.2 and 1.0, depending on standards and application.
Why pair an electric power meter with smart breakers?
The electric power meter gives you the big picture, while smart circuit breakers show you exactly where that energy is going.