In this post, we will learn the difference between MPCB and MCCB.
Circuit breakers play a crucial role in electrical systems by serving as protective switches that regulate the flow of current. They are designed to monitor specific conditions, and when a trip condition is detected, the breaker disconnects its contacts. This action effectively isolates the input and output voltages, preventing them from interacting.
A circuit breaker is an electrical device engineered for both switching and safeguarding an electrical circuit. It can function either manually or automatically to halt the current flow within the circuit. There are various types of circuit breakers available, including MCB, MCCB, MPCB, RCCB, ACB, OCB, and VCB.
Although numerous types of circuit breakers are utilized in electrical circuits, this discussion will focus on two of the most commonly used types: MPCB and MCCB.
What is MPCB?
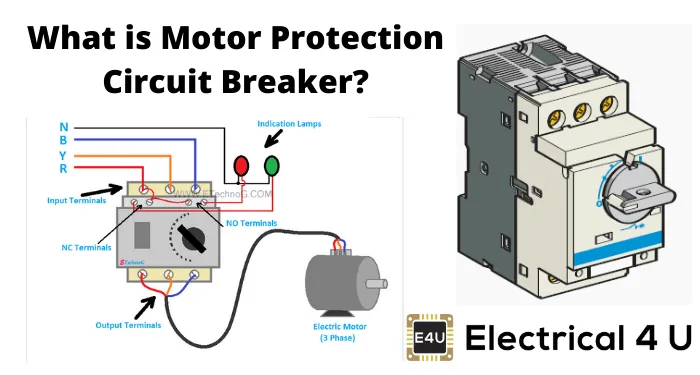
MPCB, short for Motor Protection Circuit Breaker, is a specialized circuit breaker designed to safeguard electric motors from issues such as overloads, short circuits, undervoltage, and phase loss. Essentially, an MPCB is a thermal-magnetic circuit breaker that ensures motor protection against these faults. These breakers are available for various voltage levels, typically ranging from 230 V to 660 V.
When choosing an MPCB for a specific motor, the decision is primarily based on the motor’s full load current and the highest possible short circuit current. A distinctive characteristic of MPCBs is their ability to endure the high inrush currents during motor startup without disrupting the circuit.

What is MCCB?
MCCB, which stands for Molded Case Circuit Breaker, is an electrical protection device designed to shield circuits from excessive currents due to short circuits or overloads. It employs a bimetallic strip, acting as a thermal element, along with a current-sensitive electromagnetic component for protection and disconnection. This setup allows the MCCB to guard against overloads and short circuits while also functioning as an ON/OFF switch for electrical circuits. MCCBs are versatile, operating across various voltage levels with current ratings up to 3200 A.
Widely used in heavy-duty applications, MCCBs protect capacitor banks, welding machines, electrical feeders, and motors. As a protective device, an MCCB ensures electrical safety by halting excessive current flow through circuit systems. It includes a manual switch for tripping the circuit and offers settings for both overcurrent and overtemperature conditions.
The MCCB features bimetallic contacts that expand and contract with temperature changes. Under normal conditions, these contacts allow current to flow through the circuit. However, if the current surpasses a set limit, the contacts heat up and expand until they open, interrupting the flow.


Difference between MPCB and MCCB
| Basis of Difference | MPCB | MCCB |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Motor Protection Circuit Breaker | Molded Case Circuit Breaker |
| Used for | Manually switching electric motors on/off and protecting them from faults | Switching and protecting distribution circuits and motors |
| Design Purpose | Specifically for motor protection against faults | General protection for wiring and distribution systems |
| Protection Provided | Guards motors against short circuit, overload, undervoltage, and phase loss | Protects circuits or motors from overloads and short circuits |
| Base of Setting Parameters | Based on motor’s full-load current | Set according to application needs like overload and short circuit currents |
| Selection Criteria | Chosen based on motor’s full-load current and potential short circuit current | Selected by maximum load and short circuit current it can safely interrupt |
| Function in Motor Circuit | Protects against both overloads and short circuits | Primarily guards against short circuits |
| Need of Overload Protection Relay | No additional relay needed due to built-in protection | Requires an overload protection relay |
| Auto-resetting Feature | Modern versions include auto-resetting after overload trips | Does not have an auto-resetting feature |
| Response to Starting Currents | Can handle motor’s starting inrush currents without tripping | Must be chosen based on starting current to avoid false trips |
| Need of Contactor | Optional contactor; can manually switch motors | Requires a contactor for switching purposes |
Conclusion
MPCBs have built-in overload protection, eliminating the need for extra relays and contactors, making them compact for motor use. MCCBs, however, require additional relays and contactors for motor protection, as they lack built-in overload features. This highlights the need to choose the right device based on system requirements.